Join other champions of Nearmap location intelligence
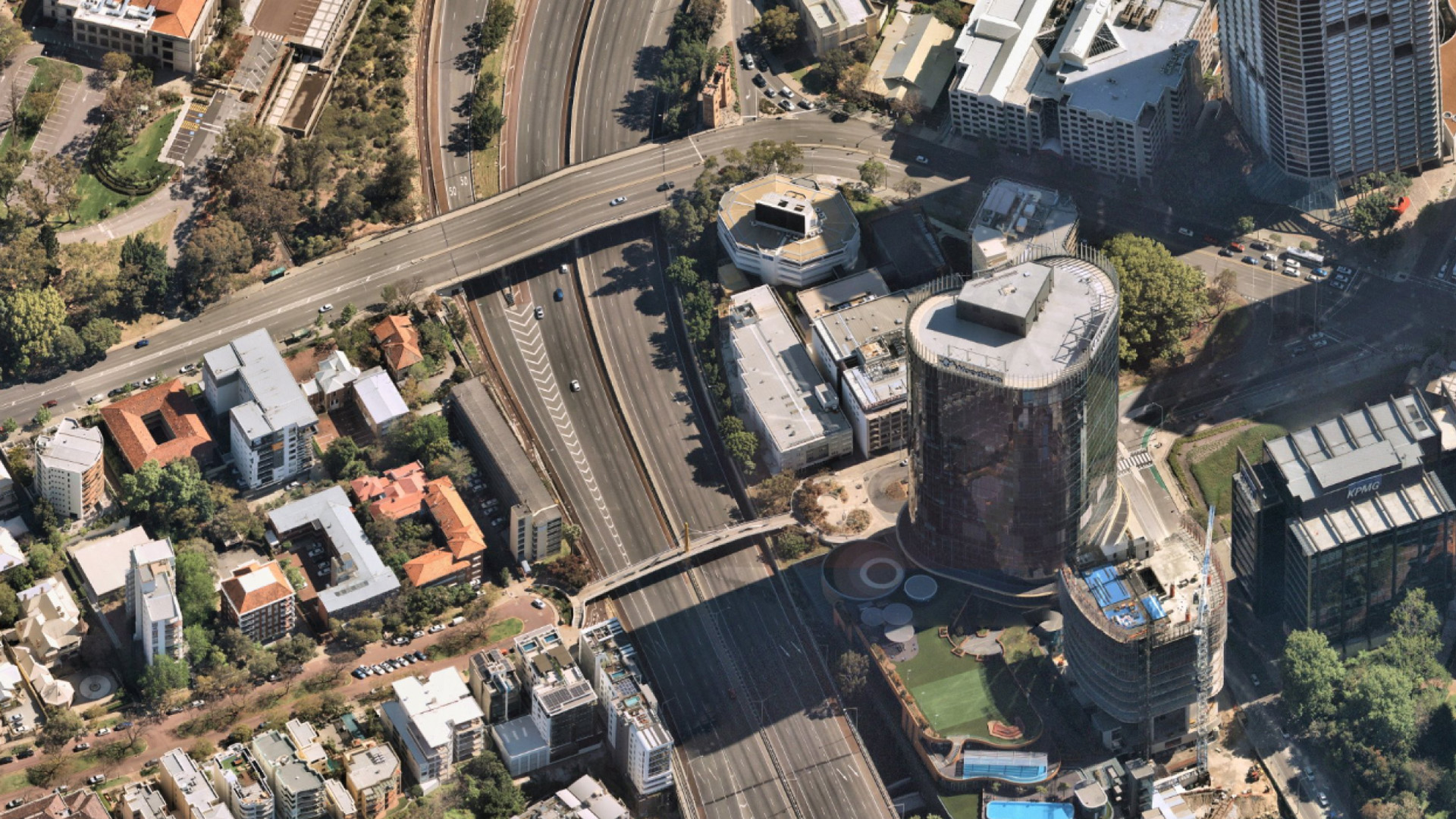

Captured by aircraft fitted with proprietary Australian-designed and built camera technology, Nearmap imagery consistently provides a ground sampling distance (GSD) of 5.5cm–7.5cm per pixel, setting it apart from satellite imagery.
Rather than enduring extended waits for updated maps, Nearmap surveys occur up to 6 times per year across metropolitan areas, capturing a current view and back-catalogue to inspect and validate changes in the built and natural environment.

Mar 2020–May 2025 | Western Sydney Airport, NSW AU
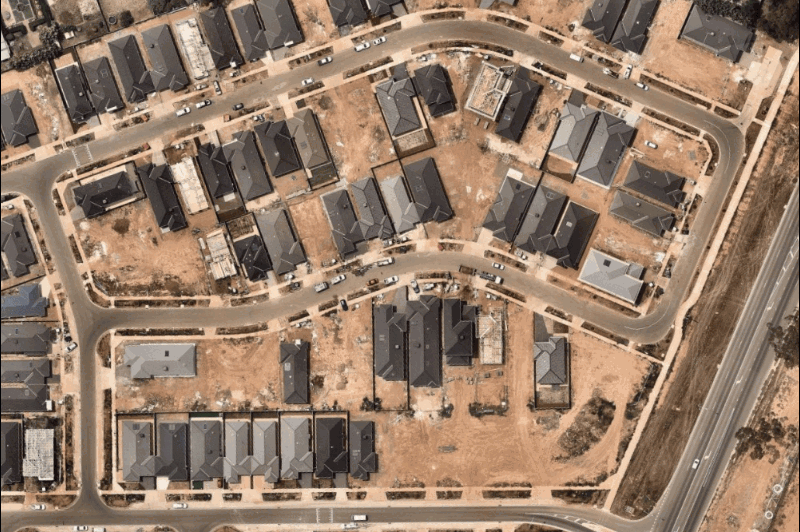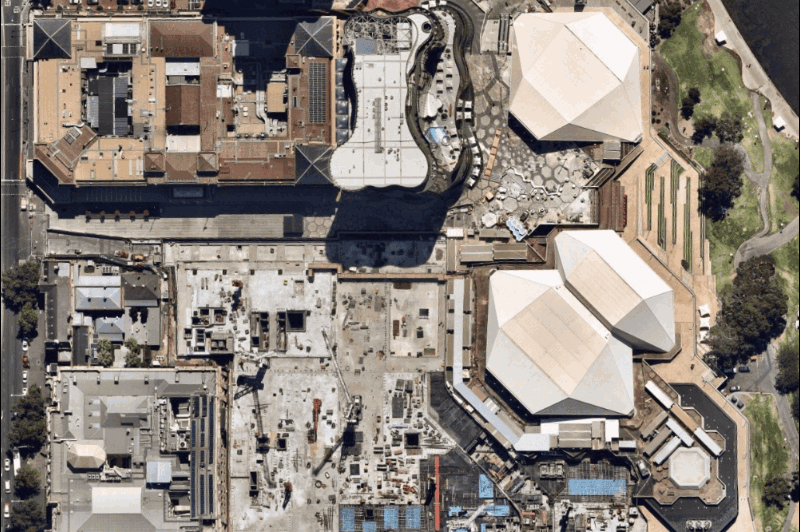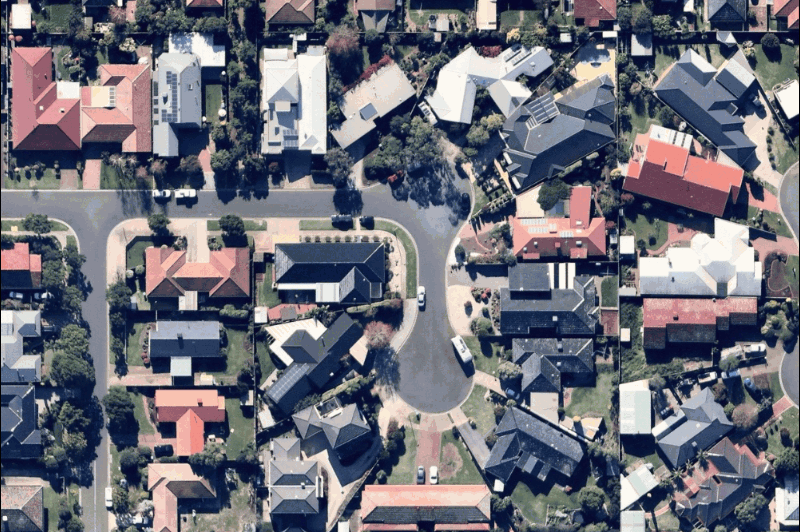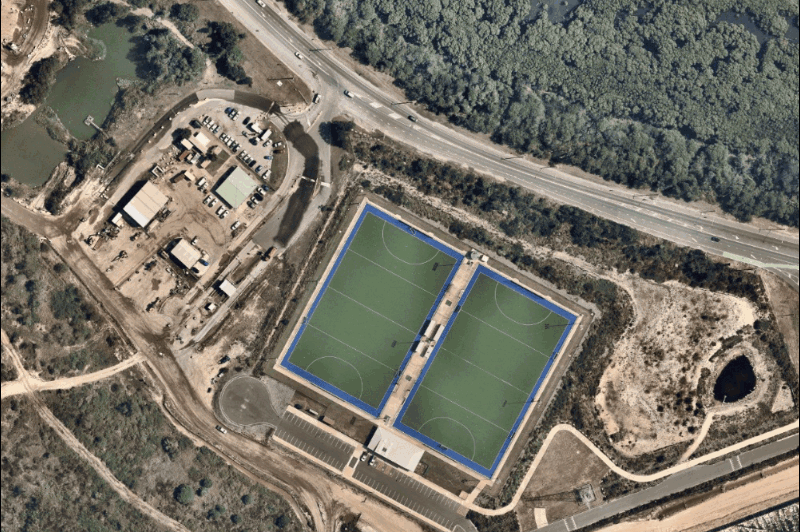
While satellite maps can be blurred by weather or atmospheric conditions, Nearmap aerial images are captured by aircraft flying in optimal weather conditions year-round, providing clarity that helps you understand critical details on the ground: buildings, assets, vegetation, water bodies, and infrastructure.
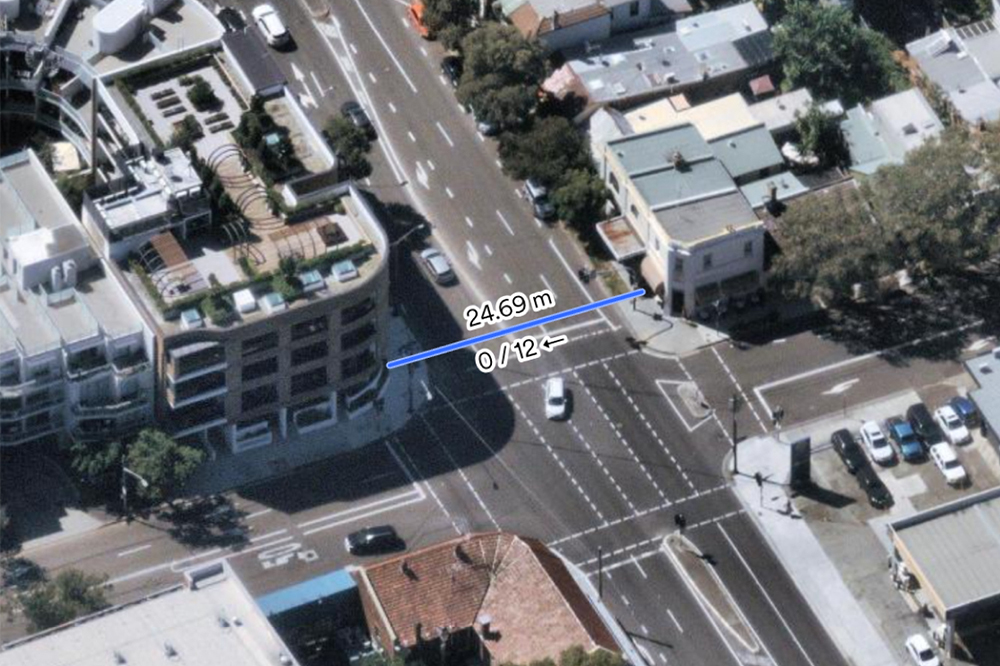
Imagery with 5.5–7.5cm GSD per pixel accuracy means you can take verifiable measurements of lines, area, radius, height, width, and roof pitch and area. Export georeferenced maps with notes, overlay other data, and save your projects in our web app, MapBrowser – making it easy to collaborate with colleagues or customers.
Aerial and satellite imagery both provide views from above — but how they’re captured, and how they’re used, differ greatly. Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide which suits your needs:
| Nearmap Aerial Imagery | Satellite Imagery |
|
|---|---|---|
| Captured by... | Camera systems mounted in fixed-wing, piloted aircraft | Electronic scanners in satellites |
| Types include... |
Vertical, Oblique, 3D, Near Infrared |
Visible, Infrared, Water Vapour |
| Best suited for.. |
Commercial applications across various industries - from construction and real estate to insurance and urban planning |
Wide-scale scientific operations |
| Advantages include... | Higher detail and more accurate |
Covers a wider area |